1031 Exchanges
1031 Exchanges: How Commercial Real Estate Investors Defer Taxes and Build Long-Term Wealth
In commercial real estate, smart investors don’t just focus on what they own today—they plan for what comes next. One of the most effective tools for repositioning a portfolio while preserving capital is a 1031 exchange. A 1031 exchange allows commercial real estate investors to sell an investment property and reinvest the proceeds into another like-kind property without paying immediate capital gains taxes. This strategy is frequently used to move between high-demand asset classes such as multifamily apartments, self-storage facilities, and mobile home parks, all known for durable demand and income stability. As of 2026, Section 1031 of the Internal Revenue Code remains fully intact, with no caps on deferred gains—making it a cornerstone strategy for long-term commercial real estate investing.What Is a 1031 Exchange?
A 1031 exchange allows investors to defer federal—and often state—capital gains taxes by exchanging one investment or business-use property for another of like kind. In real estate, “like-kind” is broadly defined. The IRS focuses on whether the property is held for investment or productive use, not on property type, size, or location. This means most commercial and investment real estate qualifies, including:- Multifamily apartment buildings
- Self-storage facilities
- Mobile home parks
- Office, retail, industrial, and mixed-use properties
- Raw or undeveloped land
How Does a 1031 Exchange Work?
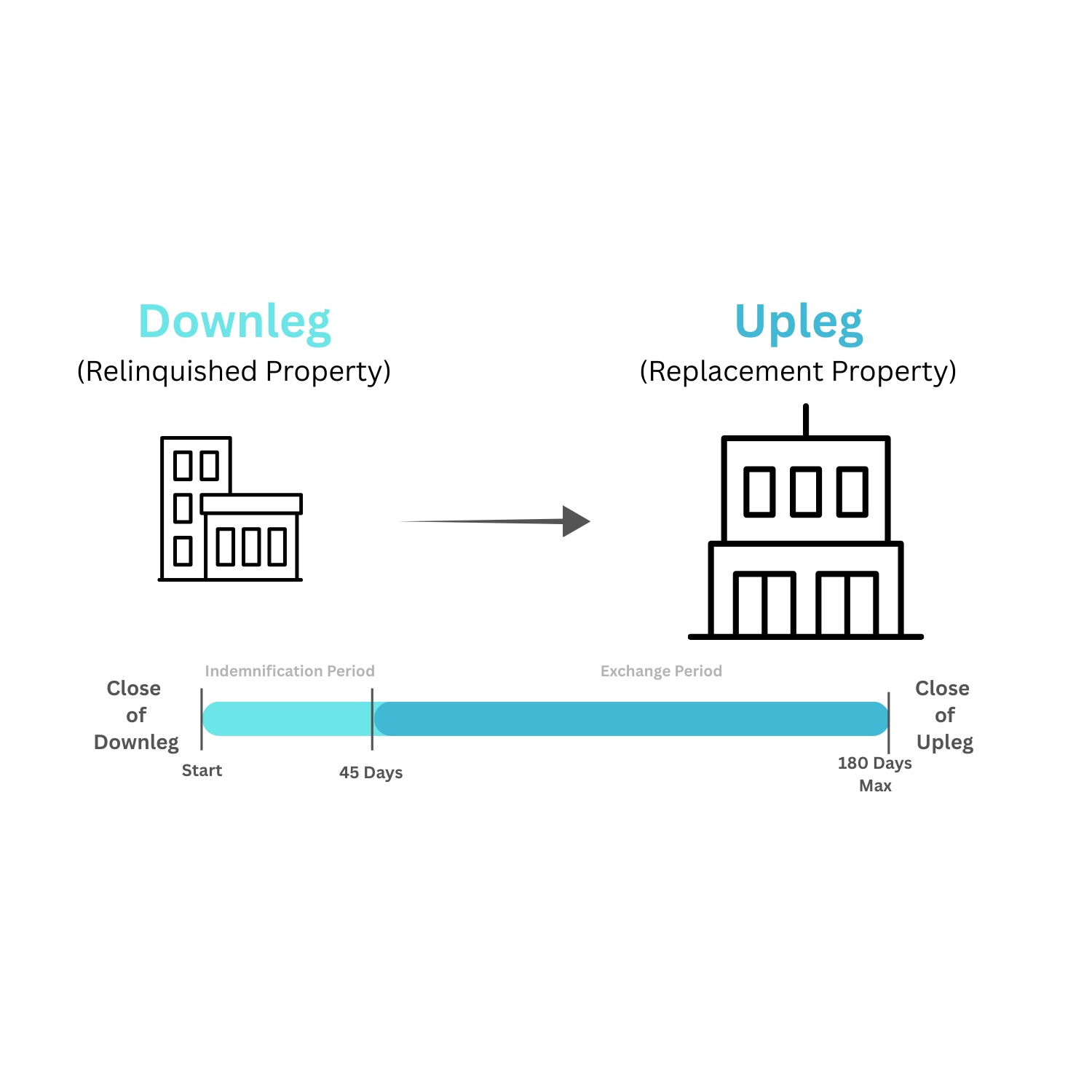
A 1031 exchange requires strict adherence to IRS rules and timelines and is typically facilitated by a Qualified Intermediary (QI)—a neutral third party who holds the sale proceeds to avoid “constructive receipt,” which would trigger taxes.Standard Delayed (Forward) 1031 Exchange Process
- Plan Ahead Consult with your tax advisor, attorney, and Qualified Intermediary before listing your property.
- Sell the Relinquished Property Sale proceeds are transferred directly to the Qualified Intermediary at closing.
- Identify Replacement Properties (45 Days)
You must identify replacement properties in writing within 45 calendar days. Common IRS rules include:
- Three-Property Rule: Identify up to three properties of any value
- 200% Rule: Identify any number of properties as long as their total value does not exceed 200% of the sold property
- Acquire the Replacement Property (180 Days) Close on the replacement property within 180 calendar days of the original sale.
Why Commercial Investors Use 1031 Exchanges
For investors focused on stable, income-producing assets, 1031 exchanges offer several key benefits:- Tax Deferral and Capital Preservation Keep more of your equity invested rather than paying 20–40%+ in capital gains and depreciation recapture taxes.
- Portfolio Optimization Reposition into assets with stronger fundamentals, better locations, or more favorable management profiles.
- Diversification Across Asset Classes Shift between multifamily, self-storage, mobile home parks, and other commercial property types based on market conditions and investment goals.
- Improved Cash Flow Many investors exchange into properties with higher cap rates or more predictable income streams.
- Estate Planning Advantages Repeated exchanges can defer taxes indefinitely and support long-term generation
Common 1031 Exchange Mistakes to Avoid
While powerful, 1031 exchanges are unforgiving when executed incorrectly. Common mistakes include:- Missing the 45-day or 180-day deadlines These timelines are strict and cannot be extended.
- Receiving sale proceeds directly Even a temporary transfer of funds to the seller can disqualify the exchange.
- Failing to replace debt properly Not matching or exceeding the original loan amount may result in taxable “boot.”
- Improper property identification Identifications must be written, timely, and compliant with IRS rules.
- Waiting too long to assemble an advisory team Successful exchanges are planned before the property is sold.